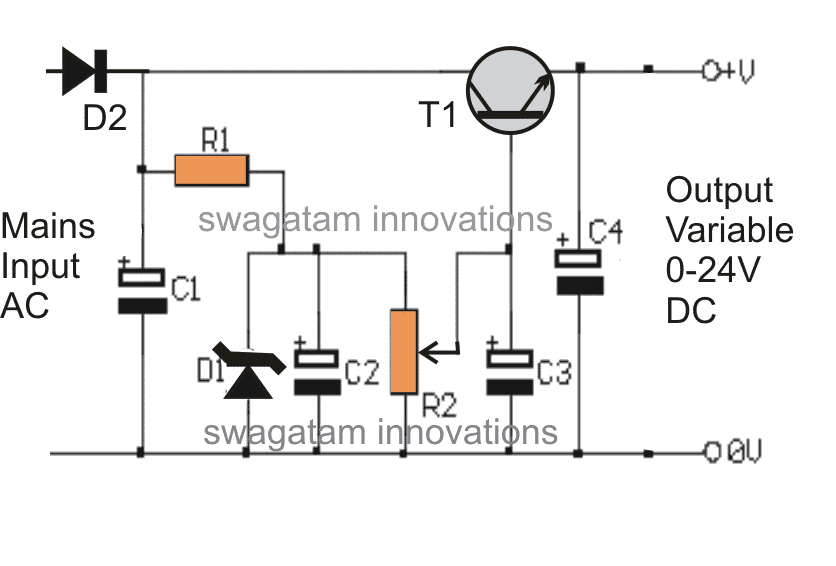
The article that you are about to read introduces a really straightforward and uncomplicated circuit for a transformerless power supply that operates on a low current from a 220 V mains source.
This circuit utilizes a budget-friendly MJE13005 transistor along with a handful of other passive electronic components.
If you take a look at the circuit diagram provided you will see that the design is incredibly simple and easy to follow.
How It Works
In this setup, the key player is the transistor known as T1 which is actually a high voltage NPN transistor called MJE13005. This component acts as the main active element within the circuit.
The other components in the circuit are arranged specifically to support T1's operation and to ensure everything runs smoothly and stably.
To break it down further, here are some important points to understand how this circuit functions:
The mains input is connected across D2 and the negative line of the entire circuit.
D2 has the job of rectifying the alternating current (AC) from the mains, while C1 works to filter it down to reasonable levels.
R1 is there to limit the current to acceptable levels so that it can provide the necessary base bias for T1.
After R1, C2 comes into play to offer additional filtering for the voltage that has been generated.
D1 serves as a clamp for the base voltage at T1 keeping it at 24V. This means that no matter what happens, the maximum output voltage will never go beyond this threshold.
There is also a mirror voltage produced at the output that matches the zener value. However thanks to R2, this response can be adjusted.
By tweaking R2 you can effectively change the zener voltage anywhere from zero all the way up to its maximum value of 24V.
As a result you can get an output that varies from zero volts up to 24 volts.
However it is essential to note that since we are measuring voltage across the emitter and ground of the transistor, the current is kept at very modest levels—specifically around 25mA.
That being said, you can increase the zener voltage as much as you want.
WARNING: This entire circuit is not isolated from mains AC power. Therefore it can be extremely hazardous to touch while it is powered on and uncovered. Please ensure that you take all necessary precautions when handling this circuit.
Parts List
| Component | Value/Specification |
|---|---|
| R1 | 100 kΩ |
| R2 | 10 kΩ POT (Potentiometer) |
| C1 | 4.7 µF / 300 V |
| C2 | 10 µF / 100 V |
| C3, C4 | 100 µF / 30 V |
| D1 | 24 V, 1 WATT Zener Diode |
| D2 | 1N4007 |
| T1 | MJE13005 |