This circuit offers a convenient solution for automatic headlight control in your vehicle. It detects the bright lights of oncoming vehicles and adjusts your headlights accordingly, eliminating the need for manual dipping.
Why You Need Automatic Headlight Dimming:
Have you ever been blinded by oncoming headlights at night? This not only creates a dangerous situation for you but also for the other driver. Manually dipping your headlights can be a hassle especially on long journeys.
Automatic Dimming is the Solution
This circuit eliminates the need, for constant manual adjustments. It uses a sensor to detect approaching headlights and automatically dims your high beams to a less glaring low beam setting. This improves visibility for both you and oncoming drivers reducing the risk of accidents.
This revised version keeps the core message about the automatic headlight dimmer circuit while making it more concise, and engaging.
How it Works:
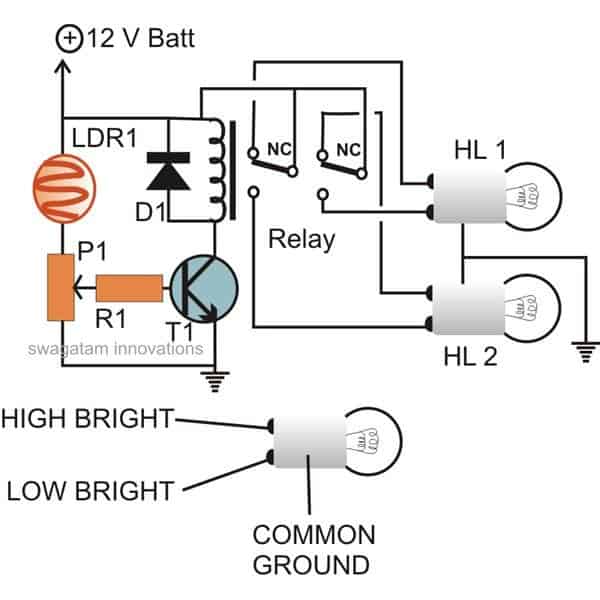
This simple diagram shows the inner workings of the automatic headlight dimmer circuit.
The transistor acts like a decision-maker, constantly comparing the light level sensed by the LDR (light-dependent resistor) with a pre-set level. It uses ground as a reference point for this comparison.
Circuit Diagram
DPDT Relay Connection Diagram with Dipper Bulb
The Light Sensor: Seeing in the Dark
The LDR or light-dependent resistor, acts like the circuit's eyes. When a vehicles headlights shine on the LDR from the front, its resistance instantly drops. This allows more current to flow, similar to how opening a valve allows more water to pass through.
Triggering the Switch: From Light to Action
The increased current through the LDR affects the transistor which acts like a switch. It flips on, activating the relay. Imagine the relay as a special button controlled by the transistor.
Headlight Dimming: Reacting to the Light
With the relay activated, its contacts switch. This reroutes the power for your cars headlight, changing them from the bright setting (high beam) to the dimmer one (low beam or "dipper filament").
Placement Matters: Seeing the Road Ahead
The entire circuit can be tucked away neatly in a small box near the dashboard. However the LDR itself needs a special spot. Its positioned outside the box, usually in a corner of your windshield. This allows it to "see" the headlights of oncoming vehicles, just like you do while driving.
Parts List
| Component | Specification |
|---|---|
| Resistor (R1) | 1K Ohm |
| Potentiometer (P1) | 10K Ohm |
| LDR (Light Dependent Resistor) | 10 to 50 KΩ (when illuminated in daylight, under shade) |
| Transistor (T1) | BC547 |
| Diode (D1) | 1N4007 |
| Relay | 400 Ohm coil, DPDT, 12V |
Alternative Design Options:
While the previous circuit uses a relay for efficient switching, alternative designs can utilize MOSFETs (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistors) for headlight control.
Using Phototransistor
The key to automatic dimming is the phototransistor labeled Q1 in the diagram. This light-sensitive switch acts like the circuit's eyes. When headlights from an oncoming vehicle shine on the phototransistor, it detects the increased light level and triggers the entire dimming process.
Setting the Sensitivity:
A resistor labeled R5 with a value of 22 Megaohms, controls how sensitive the circuit is to light. In this case, its set to react around half a foot-candle, a unit that measures light intensity. This setting balances responsiveness with avoiding false triggers from other light sources.
Powering the Switch: The Relay
The circuit uses a relay to handle the high current needed for the headlights. The chosen relay, has a 12V coil that draws 0.3 Amps. When the phototransistor detects light, and triggers the circuit, the relay switches on, rerouting power to the headlights.
Precision Optics: The Phototransistor Package
The phototransistor (L14C1) comes housed in a special package with a one-inch diameter lens. This lens focuses light onto the light-sensitive part of the transistor. The 10° angle of view ensures its primarily detecting light coming directly from the front, like headlights and not light sources from the sides.