Any kind of lead acid battery may be charged at a specific rate using the most basic lead acid battery charger circuit described in this article.
This article describes an SMPS lead acid battery charger circuit that may be used without an automatic overcharge cut-off. Why?
Simply because the maximum output voltage from the SMPS is restricted to slightly below the full charge level of the battery, which means the battery can never reach its extreme full charge level and thus an automatic cut off is avoided.
For example a 12V lead acid battery is specified with a full charge cut off range of 14.3V. But, if we charge it with a maximum of 14V then the cut off limit will never be reached and the automatic cut off may never be required.
Although, this means the battery can never attain a full 100% charging limit, the slightly lower threshold avoids complex cut-off calibrations and the lower voltage also ensures a longer battery life.
These designs have all undergone extensive testing and are capable of charging any SMF and automobile batteries up to 100 Ah and even 500 Ah.
What Does the Battery Symbol Ah Mean?
The unit used to express the capacity of a battery is Ah, or ampere-hour. It shows the optimal current rate that would allow the battery to be charged to 100% capacity or fully drained in an hour.
Using an Example to Explain Ah
Consider a battery of 100 Ah. It could potentially be fully charged in under one hour if you charged it at a rate of 100 amps. In a similar vein, the battery would only last around an hour if it were fully depleted at 100 amps.
Important Word on Safety:
A battery should never be charged or discharged to its maximum Ah rating! Your lead-acid battery may be harmed by doing this.
Ah: A Reference Point for Timing Estimation
A battery's approximate charge or discharge time at a given current rate may be calculated using the Ah rating as a reference. As an illustration, consider this:
The 100 Ah battery we used before is still in use. We can get the best charging time at a 10 amp rate by using the Ah value and the formula Time = Ah Value / Charging Rate:
T = 100 Ah / 10 amps = 10 hours
The battery may be optimally charged at 10 amps for around 10 hours, according to this calculation. But in actuality:
It might take a little longer—roughly 14 hours—to charge a fresh battery.
Rather of the recommended 10 hours, discharging may only last 7 hours.
Factors in the Real World that Impact Battery Performance:
In practical situations, no battery can function flawlessly, not even a brand-new one. The battery's efficiency and capacity may further decline with age.
Increasing the Lifespan of Lead-Acid Batteries
Since lead-acid batteries are an investment, it's critical to maximize their useful life. Avoid the temptation to use inexpensive, unproven charger designs, even if they appear straightforward. Over time, they may cause harm to your battery.
Comparing Practical and Ideal Charging
It may seem ideal to strive for the "perfect" charging technique (such as those covered on Wikipedia or Battery University), but it's not always feasible or required. These techniques frequently entail charging the battery to 14.4V, which is its maximum voltage for a 12V battery, for example.
Problems with Optimal Charging:
Using simple chargers to reach this maximum level might be dangerous. Although they can accomplish this, specialized "step chargers" are frequently difficult to construct and need exact calculations.
A Realistic Method for Optimal Charging
Here's a nice compromise: by setting the charging cut-off voltage slightly below the recommended maximum, you can still obtain "optimal" charge, or about 65% capacity. This prolongs the battery's life by reducing stress on it. The same holds true for discharge depth and rate: staying away from extremes prolongs battery life.
Charge Lead-Acid Batteries in a Safe and Easy Way
Here are some essential characteristics to search for in a charger to ensure your lead-acid battery is charged safely and dependably:
Fixed Charging Current: Approximately one-tenth of the battery's Ah rating should be consistently supplied by the charger. By doing this, undue strain and overheating are avoided during charging.
Automatic Shut-Off: When the battery reaches a certain voltage (about 17% higher than the battery's stated voltage), the charger ought to automatically cease charging. By doing this, overcharging is avoided, which can limit the battery's lifespan and cause damage.
Optional Float Charge: Some chargers provide a "float charge" mode, albeit it's not necessary. In order to keep the battery fully charged for extended storage without overcharging, this maintains a low voltage level.
- With a battery specified at 12 V and 100 Ah, for instance, the fixed input voltage should be about 14.1 V, or 17% more than the stated number (not 14.40 V, provided you are working with a step charger).
- In our situation, current (ampere) can be 10 amperes as the optimal value is 1/10th of the Ah level indicated on the battery. Given that our full charge level is currently lower, a somewhat higher amp input may be acceptable.
- While charging auto cut off is advised at the previously indicated 14.3 V, it is not required because we now have the full charge level somewhat lower.
- Once the battery is fully charged, the procedure known as "float charge" involves lowering the current to extremely small levels. This keeps the battery from self-draining and maintains it at full capacity until the user removes it to use. It is entirely voluntary. Only if you are not using your battery for extended periods of time might it be required. It is also preferable in these situations to take the battery out of the charger and top it off once every seven days.
As we shall see below, utilizing voltage regulator integrated circuits (ICs) is the simplest technique to obtain set voltage and current.
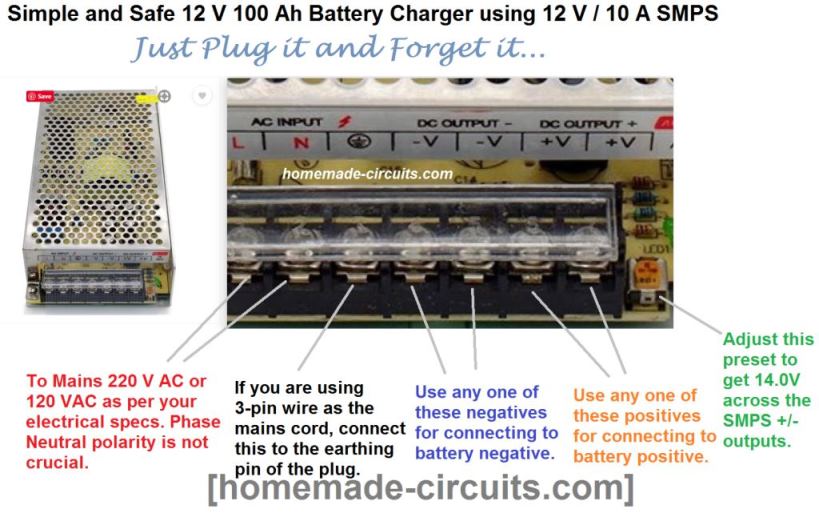
Using a ready-made 12 V SMPS 10 Amp device with an adjustable preset as the input source is another simple method. A little setting in the corner of the SMPS may be adjusted to 14.0 V.
Keep in mind that you must leave the battery attached for a minimum of 10 to 14 hours, up to the moment the voltage at the battery's terminal attains 14.2 V.
This level makes sure your battery will never become overcharged and promotes a long life for the battery, even if it may appear somewhat undercharged compared to the typical 14.4 V full level.
This infographic below provides all the information: