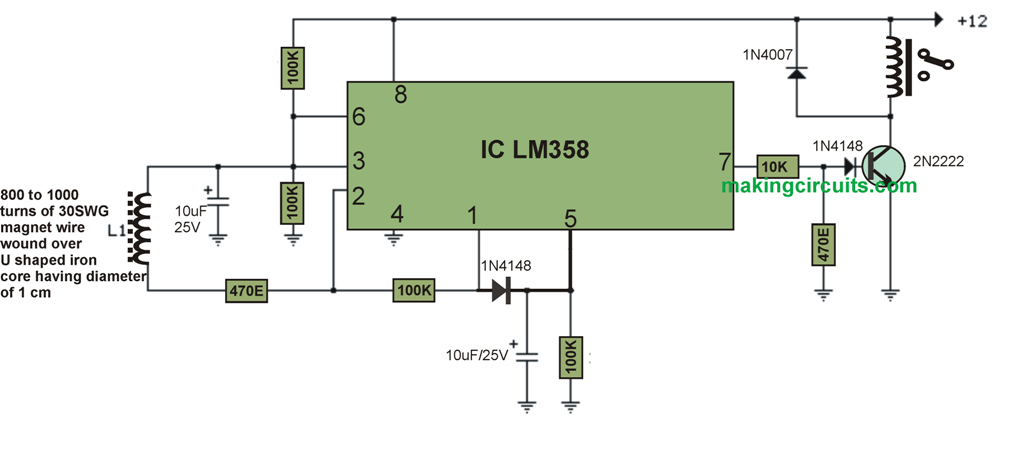
This AC mains current detector circuit identifies current levels within one of the AC mains supplies with the aid of an inductive pickup sensor (L1) made using a one inch diameter U-bolt wrapped with eight hundred spins of 30 SWG super enameled wire.
It senses AC mains line currents of approximately 200 mA or maybe more without requiring any specific electrical connectivity to the supply. The sensing could possibly be composed of different iron variety rings or transformer cores allowing you adequate room to cross any of the AC lines via the core.
Just one of the current bearing lines, possibly the phase or the neutral need to be positioned via the central part of the sensor to steer clear of the magnetic flux cancelling.
I certified the proposed AC mains current circuit working with a a couple of cable prolongation which I had set apart the double wires a tiny length with a multi tool to enable the U-bolt to encircle just one cable.
The magnetic pick-up sensor (U-bolt) generates approximately 4 millivolts maximum for a AC mains line current of 250 mA, or AC load of close to thirty watts.
The transmission from the sensor is enhanced roughly two hundred times at the end result of the op-amp pin 1 that may be consequently peak determined by the capacitor and diode connected to pin 1. The 2nd op-amp is used within the IC as a comparator which picks up a voltage increase more than the diode drop.
The minimal transmission necessary to bring about the comparator stage output to turn positive is approximately 800 mV maximum which amounts to roughly a 30 watt load on the Alternating current line.
The output of 1458 op-amp is only going to fluctuate within a few volts of negative hence a voltage divider (1K/470) is employed to bring down the no-signal voltage to approximately 0.7 volts.
A supplementary diode is inserted range with the transistor base to guarantee it switches off the minute the op-amp voltage is 2 volts. You can receive a small amount of relay stuttering in case the AC load is adjacent to the changing over level as a result a more substantial load of 50 watts or even more strongly suggested.
The level of responsiveness of this AC mains current circuit may very well be augmented by contributing more number of turns to the pickup coil.
Hello Admin,
Thank you for sharing this circuit!
Would it be possible for you to make a re-settable fuse based on this? I’m hoping for something with adjustable current cut-off in the range of 1 amp to 10 amps.
This will be useful when troubleshooting or testing appliances like microwave ovens that blow fuse, for example.
Thank you.
Hello Mark, do you want the the circuit to latch and switch OFF in response to a current, which can be then reset manually?