It is very necessary that this electronics enthusiast needs a constant current source.
If this type of need does occur, for instance for test requirements, it can be a item of equipment which is not normally accessible.
On the other hand, it is far from essential to create a entire constant current source for every application.
It is sufficient to have a adapter which can be linked to an available power supply whenever a constant current source is essential.
The recommended constant current adapter circuit has yet another beneficial application: the asymmctric-to-symmetric power supply converter at the front end of the frequent current adapter can be utilized independently to power an amplifier or related circuit.
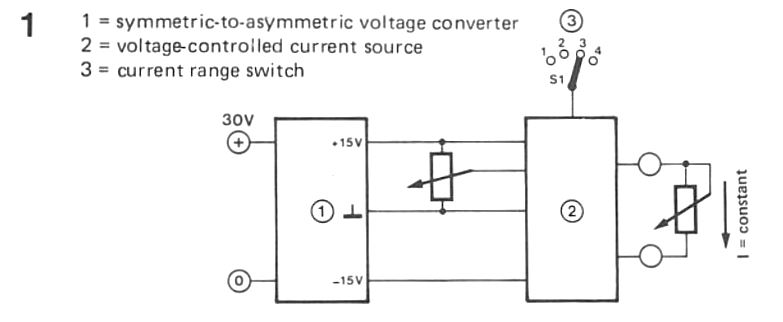

Most amateur constructors use a mains power supply using a variable output voltage as high as 30 V and a current output of around 200 mA (or higher).
This particular supply then can be employed to power the constant current adapter.
The asymmetric-to-symmetric converter including IC1 and transistors T1 and T2 offers an efficient output voltage of ± 15 V over the two capacitors C2 and C3.
This particular shaped supply can be employed individually provided the necessary output current is no higher than about 50 mA.
How the Circuit Works
We will right now analyze the constant current adapter itself in better aspect.
The asymmetric-to-symmelric voltage converter is needed to power the functional amplifier IC2.
This opamp can be used as the current source and is also regulated by the potential divider composed of potentiometer P1 and resistors R3 and R4.
Potentiometer P1 are adjustable to offer an output voltage of between 1. 5… 15 V. A constant current will certainly flow by means of load resistor R1, which can be determined by the voltage setting of P1 and on the range picked by switch S1.
The Constant current adapter circuit is certainly that, inspite of the specific range, the current via R1 is dependent upon the setting of P1.
Transistors T3 and T4 just form a buffer level.
The output current of the adapter could be worked out through the formula.
I = 0.1 x UP1 / R10 or R11 or R12 or R13
Potentiometer P1 ought to discover a range from 1 to 10 in order that it is a lot easier to manage the specified current.
Based on the setting of the range switch S1, the current can then be deduced using the multiplication element presented in the table below.
Potentiometer P2 needs to be altered in the beginning in order that an output current of 10 A is acquired when SI is in position '1' and P1 is placed at minimum output
Leave a Reply