This is a novel music level indicator, ideally suitable for using in a place like discotheque. This indicator is made of eight columns of eight LEDs are being placed at equal distance, so that it looks like a star. The corresponding LEDs in the eight column form concentric circles as shown in the following figure.

The higher the sound level, there are more circles light – resulting into a star-alike pattern with constantly changing brightness.
PLEASE COMBINE THE TWO IMAGES BELOW TO COMPLETE THE FULL CIRCUIT SCHEMATIC OF THE PROPOSED DISCOTHEQUE MUSIC LEVEL EFFECT GENERATOR CIRCUIT
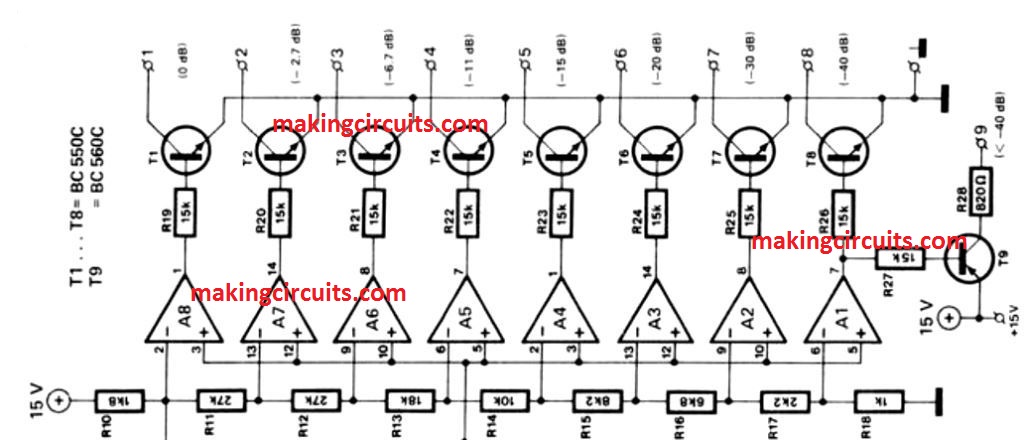

As depicted in the first figure, the eight LEDs in anyone of the eight circles are joined in series. Transistor in the above circuit schematic drives each of these series chains, for instance T1 to T8.
It is not required to drop the resistors: over 1.8v per LED is provided by the positive supply voltage – this voltage is perfect for LEDs to function properly.
How the Circuit Works
Differential amplifiers, i.e. A1 to A8 drives the Transistors T1 to T8 : the amplifiers compare the direct voltage across C2 and the direct voltage is dependent on the audio. C2 is buffered by A12, with the potential which is determined by D11 and from R11 up to R18. When the result of the comparison comes positive, the associated driver transistor is being turned on, as well as the appropriate circle of LEDs. D4 which is the LED in the centre is driven by T9 and the light only gets turned on when the sound level is significantly less.
The direct voltage which runs across C2 results from a full-wave rectification in A10 , as well as A11 of the input signal only after it is amplified in A9. For saturation, the sensitivity of the input value mist be about 600mV which is required to turn on all 64 LED lights. However, the number can be increased by decreasing the value of R2.
The speed with which variation in music level is displayed, relies on the value of C2: if the value is 10µF, there is a slow change in light patterns. On the other hand, when the capacitor is omitted, it readily reacts to variant sound changes.
PCB Designs
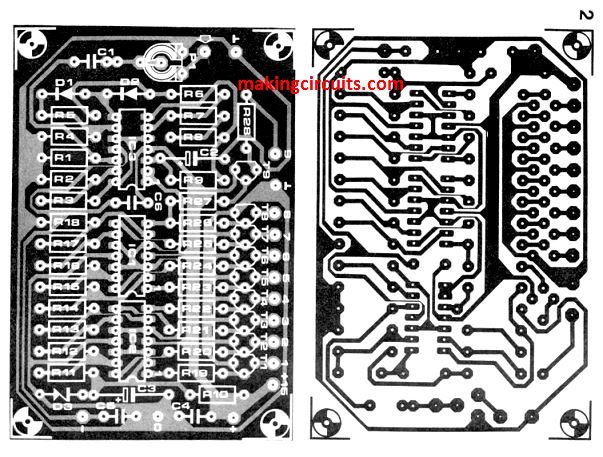
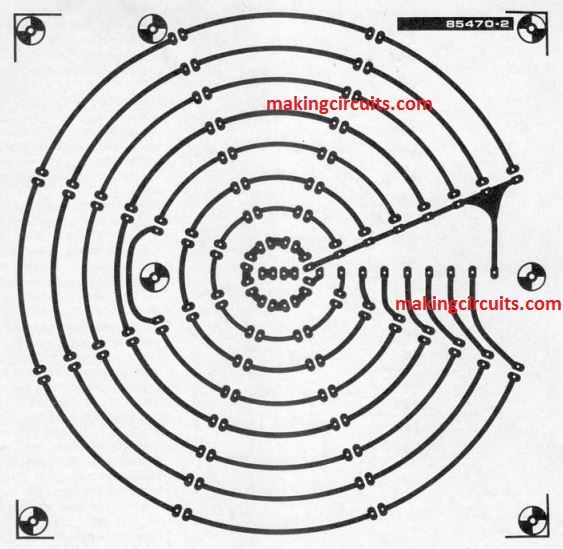
The discotheque music level indicator circuit is created on two printed circuit boards as indicated above. The LED board as shown above doesn’t comprise of a component layout since it didn’t look aesthetically attractive. One can fit the two boards together with the use of spacers: exact holes are being given for this in a pattern which makes sure that all the 11 terminals for interconnections on the board remains opposite to one another.
also can i have a high res image i want to try this for my college project
hi can you connect the two diagrams and label the Audio input
There are only two connections to be made between the upper diagram and the lower diagram, also make sure the positive and the negative supplies are connected for both the diagrams.
Audio input is across P1 preset