The simple circuit presented in this article safeguards a lead acid battery from self-discharging, especially when the battery is not being used or charged for long periods of time.
The unit not only protects the battery from self-discharging, it keeps the battery fully charged and in a topped up condition, thus maintaining an overall good health for the battery in all conditions.
This circuit is very useful for maintaining lead-acid batteries that are lying dormant for a long time but still work.
The circuit charges the battery and lets it discharge slowly using the internal resistance of the battery itself and the circuit.
Once a state of charge or the SoC is met, the charger is switched on again. The battery will be charged again and the whole process repeats continuously.
How the Circuit Works
Reffering to the schematic below, the unit is built using a Schmitt trigger T1/T2 Zener, the circuit also consists of Zener diode D7 that sets the state of charge where the charger is turned off. Resistor R2 supplies the needed hysteresis.
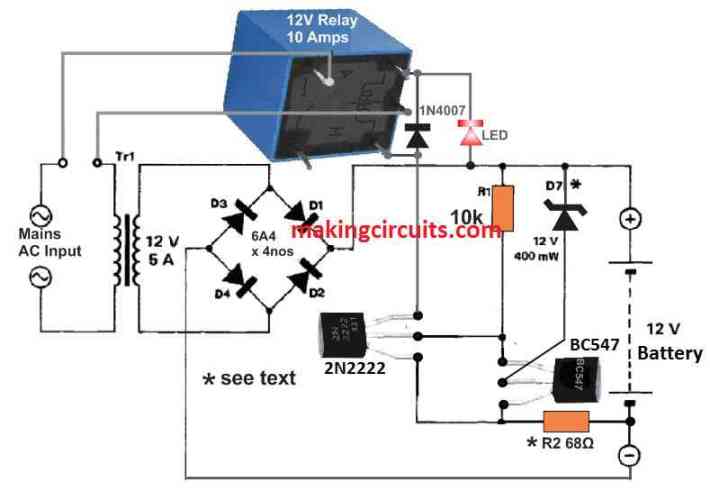
Since the mains is disconnected and there is no battery attached to the respective terminals, examine if the relay switches on and off using voltages from a regulated power supply.
How to Set Up
To set up this self-discharge battery protector circuit, adjust the voltage so that 13.6 V and 12.5 V are placed across the battery terminals. You can tune the ‘on’ threshold by attaching a 1N4148 (cathode to the positive line) in series with D7. The ‘off’ threshold value can be adjusted by modifying the R2 value. For instance, you may replace this resistor with a 100-ohm preset.
There is also a possibility of replacing the mains transformer and bridge rectifier with a battery charger.
With this setup, the rest of the circuit can be assembled into the charger.
But remember, it is impossible to connect a completely discharged battery (below 10V) to the circuit because the relay will not be energized.
Instead, you should charge such a battery to more than 10 V. Another workaround is to place a switch in parallel with the relay contact and turn off the mains using the switch.
Using Two Batteries
You could also maintain and protect self-discharge for two 12 V batteries on a condition that the secondary voltage of the mains transformer, the Zener voltage of D7, the hysteresis and coil voltage are doubled.
Besides, you must ensure the batteries are connected in series across the terminals. We recommend using fuse F1 to safeguard the components against a short-circuit.
You can also do the same for protecting the transformer primary circuit using a 1 A fuse. Since the whole activity revolves around the battery, a smoothing capacitor is not required by the circuit.
Leave a Reply