An LC meter or Indictance/Capacitance meter is multipurpose measuring device which is ued for identifying unknown inductor and capacitor value quickly.
An LC meter is without any doubt essential to anybody associated with electronic circuits.
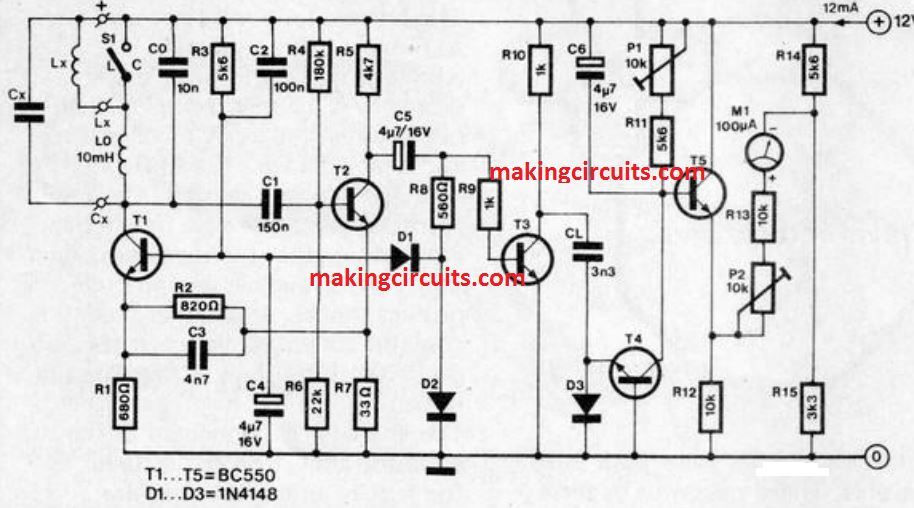
Explained circuit takes the unknown inductance, La, or capacitance, CO, within a 2 transistor oscillator circuit, in which the output voltage is held constant between 30 and 40 mV through a regulator.
If, in the oscillator circuit, Ca is attached in parallel with capacitor Co. or La in series with inductor L0, the frequency of the circuit decreases. This diminution is assessed by a frequency -to -voltage converter, T3/T4. The resultant output voltage of emitter follower T5 is utilized to stimulate meter M1.
Meter M1 is hooked up on the diagonals of a bridge circuit, in order that it shows zero when Ca or La is non existent. The meter is fixed to full-scale reading f.s.d.1 through P2 in case either La = Lo or Ca = Co is introduced into the oscillator circuit.
The threshold of frquency determining capacitor CL in the frequency-to-voltage converter is balanced out by P1.
It is as a result essential to switch with a new 10 k preset for every single measuring range, and anytime this is carried out the f.s.d. must be fixed freshly with P2.
The magnitudes supplied in the circuit for Lo and Co are legitimate for a f.s.d. of 10 nF or 10 m1-1. A highest number of 9 testing ranges could be made available from a 4 way, 9 position rotary switch.
The magnitudes of L., Co CL, and the corresponding frequency, without having Lx or C and at full-scale deflection, are listed in the table. The precision of the readings, provided cautious calibration, is approximately 3 %.
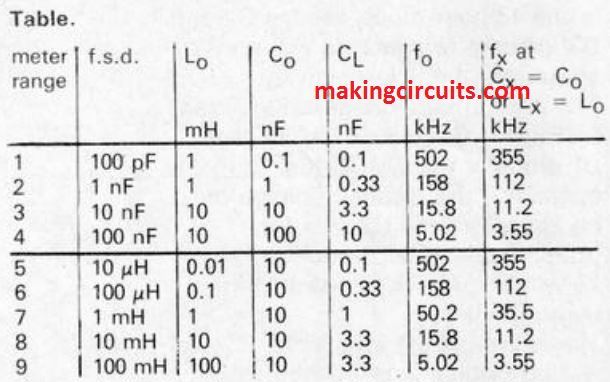
Markings of the range is close to sufficient equal for all ranges, however is 'extended' by a element of about 3 for lower measurements.
This needs, of course, an appropriate correction. Calibrating the scale may be carried Out with a table compiled with the formula ni = nm(1-fr)/(1-fc), where
- ni = number of scale divisions indicated
- nm = number of scales divisions at FSD
- fr = relative frequency
- fc = lowest relative frequency
Total current consumption amounts to about 12 mA at 20,
Leave a Reply