The majority of the Hi Fi amplifiers being used derived from circuitry such as this layout, even though they tend to be more modern.
The 1 watt amplifier circuit utilizes a 'complementary' output stage, along with one NPN and one PNP power transistor, which often gets rid of the importance of an output transformer located in old amplifier models.
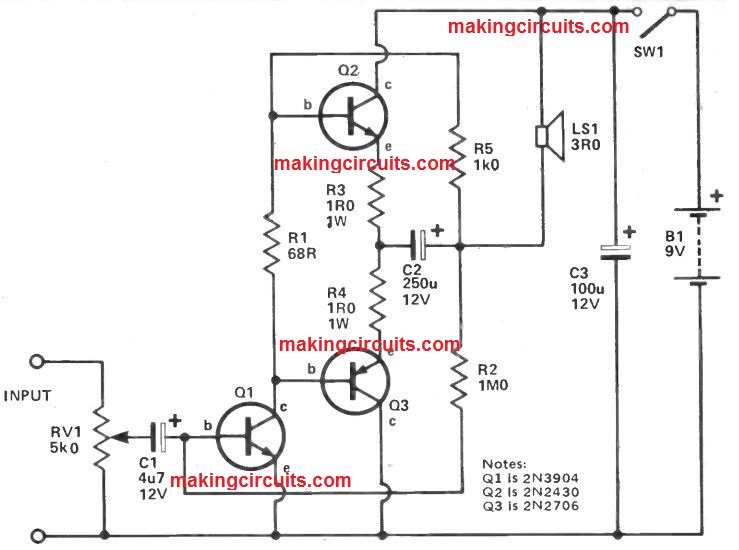
Output power is near to 1W, with realistically lower distortion. The input signal is that passes the volume control RV1 after which through C1 to the base of Q1.
The collector load for Q1 consists of R1, R5 and also the loudspeaker and the voltage at the collector will probably be around half the supply voltage, i.e. 4V5.
The bases of Q2 and Q3 can also be additionally to voltage (quite close to) since the collector of Q1 since the value of R1 is really low (68R).
At the junction of the emitters of Q2 and Q3 the voltage may also be quite close to 4V5, R3 and R4 and really low value resistors to restrict the current via Q2 and Q3.
Once the amplified input signal is no more than 4V5, Q2 is switched off (since the base will probably be at a lower voltage compared to its emitter), however Q3 will certainly perform the signal.
When Q1 amplifies the signal to over 4V5 the change occurs, Q2 performs and Q3 is switched off. The signals are merged at the the normal emitter junction of Q2 and Q3 and passed to the loudspeaker with the significant electrolytic capacitor C2.
Small values of C2 end up within a bad lower frequency result. Negative feedback is supplied by R5 and R2, all these make sure that firmness by decreasing the gain marginally.
In this 1 watt amplifier circuit R1 is incorporated to present quite a few base bias for Q2 and Q3; more modern layouts employ thermistors or diodes to stop thermal runaway' which could eliminate the output pair.
A drawback may be the DC coupling of the transistors, if one transistor alters its features the outcome could be devastating!
Because of this, the output pair can be quite a 'matched pair', other forms could be attempted provided that will not have the "matched pair"
Leave a Reply