Using the explained transmitter and receiver circuits, you can quickly exploit the existing mains home AC wiring to send signals across different rooms, for remotely switching ON/OFF any desired appliance such as lights, fans ACs, heaters, between rooms of your house.
This home power line remote controller circuit combines the transmitter and receiver protocols based on your home’s mains power network for remote control of the single-phase household appliances.
Transmitter Circuit
In the first figure below, a transmitter is represented. This device overlaps a 36 kHz signal on the 50 Hz AC voltage of your home when switch S1 is actuated.

Then, IC1 is supplied the voltage from the mains through rectifier circuits that comprise D1, D2, Zener diodes D3 and D4, and a filtering capacitor C4. We recommend to set up the circuit with +20V supply concerning the mains network-neutral (0V) line.
The opamp generates the 36 kHz signal and it is channeled to the mains using a coupling capacitor, C3. A bleeder resistor, R3, is used to discharge C1 and C2 when you uncouple the circuit from the AC voltage.
Receiver Circuit
In the next receiver circuit diagram below, it is supplied with a cost-effective doorbell transformer but any other power supply that can give out 6 to 8 V AC at around 0.3 A works just fine.
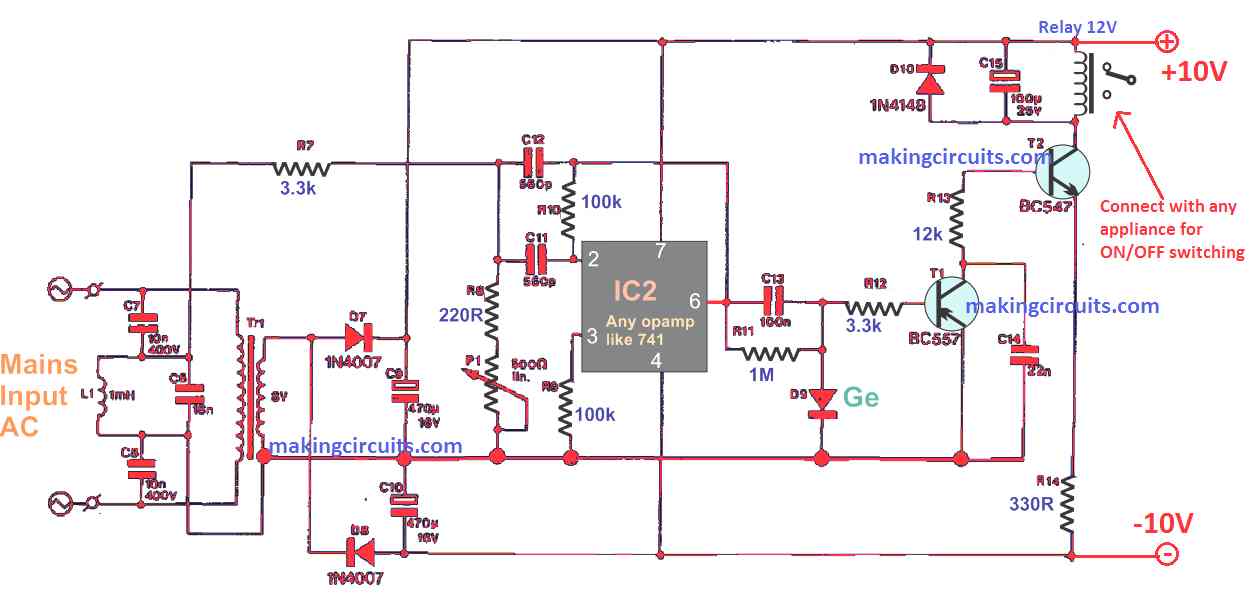
Besides driving Tr1, the AC voltage with the 36 kHz carrier is filtered by a circuit of L1-C6 which is connected in parallel.
This small section of the entire network functions to sense the existence of the overlapped 36 kHz carrier which is directed to amplifier IC1 through resistor R7.
After effective rectification by D9, the relay driver circuit which consists of T1 and T2 becomes enabled to energize Re1.
D9 should be preferably a germanium diode such a OA79 or similar. If you don't get this, a simple 1N4148 might do the job as well.
Afterwards, preset P1 is regulated to determine the correct cooperation between the sensitivity of the receiver and the noise resistance. When choosing the value for R14, make sure to consider first the relay coil current.
How to Install
Fundamentally, the implementation of this Power line AC remote controller circuits an entirely secure con-ABS case is utilized to avoid accidental contact with the AC voltage wires.
This step is always obligatory when working with any mains voltage circuits.
After this is verified, the transmitter can be mounted on a spare adaptor case with a small opening for attaching switch S1.
The ABS case of the receiver is expected to bigger if the mains socket is included for simpler connectivity with the household appliance to be controlled.
Be mindful of the rating of relay Re1 if you plan to switch heavy loads, like the coffee machine which houses a current of 4A.
Leave a Reply