The post discusses the complete datasheet of the transistor 2N3904.
Electrical Characteristics (TJ = 25°C unless otherwise noted)
- Collector-Emitter Breakdown Voltage (V(BR)CEO): 40-60V
- Collector-Base Breakdown Voltage (V(BR)CBO): 60V
- Emitter-Base Breakdown Voltage (V(BR)EBO): 6V
- Collector-Emitter Saturation Voltage (VCE(sat)): 0.2-0.3V
- Base-Emitter On Voltage (VBE(on)): 0.65-0.85V
- DC Current Gain (hFE): 100-300
- Collector Cutoff Current (ICBO): 50nA max
- Emitter Cutoff Current (IEBO): 50nA max
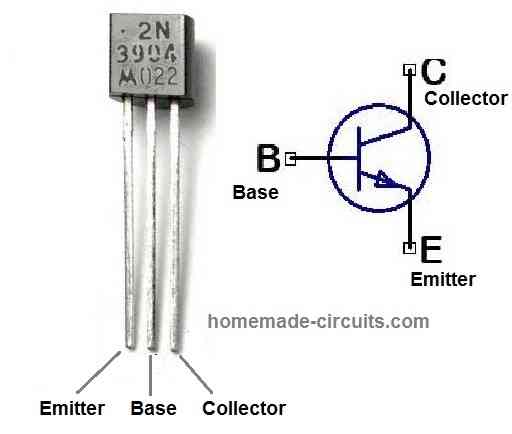
Pinout Configuration
The following image provides the pinout details and configuration for the transistor 2N3904.
Absolute Maximum Ratings
- Collector-Emitter Voltage (VCEO): 40V
- Collector-Base Voltage (VCBO): 60V
- Emitter-Base Voltage (VEBO): 6V
- Collector Current (IC): 200mA
- Base Current (IB): 20mA
- Power Dissipation (Pd): 625mW
Miscellaneous Information
- The 2N3904 is a general-purpose NPN bipolar junction transistor (BJT).
- Its package type is TO-92, which is a popular small signal package used for transistors and other electronic components.
- The maximum power dissipation of the transistor is 625mW, which means it can handle up to 625mW of power before it begins to overheat.
- The maximum collector current of the transistor is 200mA, which means that it can handle up to 200mA of current flowing through the collector terminal.
- The maximum collector-emitter voltage is 40V, which means that the transistor can handle up to 40V between the collector and emitter terminals before it breaks down.
- The DC current gain of the transistor is typically between 100 and 300, which means that the current flowing through the collector is amplified by a factor of 100 to 300 times the current flowing through the base terminal.
- The transistor can be used in a wide range of applications, including amplification, switching, and oscillation. Its low cost, small size, and versatility make it a popular choice for hobbyists and professionals alike.
Leave a Reply