Lead-acid batteries that remain unused for a long time will inevitably go bad. The self regulating battery charger circuit explained below is meant to keep such a battery healthy through the period of dormancy.
The circuit charges the battery and then allows it to discharge through itself as well as the internal resistance of the battery. Once the charge sinks below a certain level, the circuit once again charges it, thus continuing the cycle.
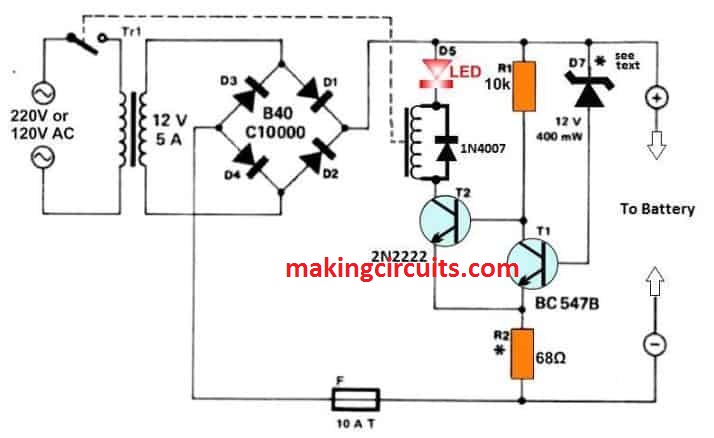
How the Circuit Works
The circuit works on a Schmitt trigger T1/T2. The charge at which the charger needs to switch off depends on the D7 Zener diode, while the necessary hysteresis is supplied by the R2 resistor.
Test the circuit by applying voltages of 13.6 V and 12.5 V across the battery terminals without the mains or any battery connected to it. The relay should switch off and on respectively.
The critical value for switching the charger on may be fixed by connecting a 1N4148 (cathode to + line) to D7 in series. The value for the off state can also be changed by varying R2, say by putting in a fixed 100 Ω resistance in its place.
Another possibility is using a battery charger in place of the bridge rectifier and the mains transformer, retaining the rest of the circuit and connecting it with the charger.
Keep in mind that the circuit will not work with a fully discharged battery - it must at least be charged to over 10 V. An alternative is to switch on the mains using a switch connected in parallel to the relay contact.
How to Charge two Batteries in Series
You can also maintain two 12 V batteries this way through automatic self regulation of their charging voltage, so that none of them over charges.
For this all you have to do is to raise the mains transformer secondary voltage, the D7 zener voltage, the voltage of the ralay coil and the hysteresis.
The circuit is completed by fitting both batteries across the terminals in series.
The circuit is protected against short circuits using the fuse F1. The same can be done for the transformer primary circuit using a delayed action fuse like F1 with a threshold of 1 A.
A smoothing capacitor is redundant here as the battery itself does that job.
Good evening sir. Please I was reading about the self regulating battery charger. I don’t know much about electronics. How do I modify it to charge two 12 volts in series. The Ah is 200 each.
Thank you. Please reply with the circuit diagram. My email address is: dkabbey1959@gmail.com
Daniel, you can add two 12V in series, by modifying the zener diode accordingly by using a 25V zener, the relay will also need to be modified and replaced with a 24V relay. Needless to say the transformer will also need to be replaced with a 24V transformer. 68 ohms can be increased to 100 ohms