Diodes are divided into two categories: germanium diodes and silicon diodes, with the silicon diode being the most popular. In germanium diodes, forward conduction starts at around 0.2 V. This starts at around 0.6 V in silicon diodes.
In comparison to silicon diodes, germanium diodes have a higher reverse leakage current. When germanium diodes are exposed to the peak (highest permissible) inverse voltage, or PIV, the leakage current ranges from 0.25 mA to 1 mA.
We would be discussing 2 main rectifier diode parameters or specifications, which include PIV and IF .
PIV stands for peak inverse voltage which signifies the maximum reverse bias voltage or reverse blocking voltage a diode can tolerate, exceeding which the device can burn or break down..
IF refers to the forward bias current that a diode is able to tolerate, exceeding which the device can get permanently destroyed.
Signal Diodes and General-purpose Diodes
General purpose diodes such as the 1N4148 or 1N914 can be used for a wide variety of applications such as clamping, clipping, biasing, logic, and op amp rectifiers. These feature a PIV of 75V and can deliver a forward current of up to 100 mA.

The 1N916 is a low-capacitance variant of the 1N914.
The BY206 (IF = 400 mA, PIV = 350 V) is a general-purpose diode with bigger ratings.
You can use the diode BAS16 (IF = 0.6A, PIV = 85V) or the BAS28 dual diode for surface mount technology SMD).
You can use a Schottky diode, including the BAT42, for a reduced forward voltage drop (0.4V at 10mA) and high speed switching time. Schottky diodes have low PIV and increased reverse leakage, which are its drawbacks.
If a germanium diode is desired, the OA91 or an equivalent diode should be used. The OA47 is a germanium diode with a reduced VF (0.4V at 10mA) and a high speed switching time and can be used for detection function in radio receiver circuits.
Rectifier Diodes
The 1N4000 and 1N5400 series rectifier diodes are the most common, offering peak forward currents of 1A and 3A, respectively. The ultra fast UF4000 and UF5400 series with 50 ns recovery time are the equivalent counterparts, for fast switching applications like switch mode power supplies.

The last digit of the type number indicates the PIV for the 1N4000 series: 1 = 50V, 2 = 100V, 3 = 200V, 4 = 400V, 5 = 600V, 6 = 800V, 7 = 1000V. The PIV of the 1N4006 is 800V, for example. The comparable numbers in the 1N5400 series are: 0 = 50V, 1 = 100V, 2 = 200V, 4 = 400V, 6 = 600V, 7 = 800V, 8 = 1000V. The PIV of the 1N5406, for example, is 600V.
Whenever quick switching is required, Schottky barrier diodes such as the MBR150 and MBR350 rectifier diodes can be extremely helpful. They feature reduced forward voltage loss and are capable to withstand 1A and 3A currents, respectively (at approximately 0.7V at maximum forward current, in contrast to 1.1V for the 1N4000 and 1N5400 series rectifier diodes).

Schottky barrier diodes cannot, however, tolerate large reverse voltages (PIV = 50V). They're especially well-suited to low-voltage, high-current supplies.
There are many more rectifier diodes that can operate with higher voltages and currents than the ones mentioned in the above discussion. When running at high power, stud-mounting varieties should always be connected to heat sinks.
A bridge rectifier, which consists of four such rectifier diodes fully integrated into a full-wave bridge, can be a good substitute to employing single diodes.
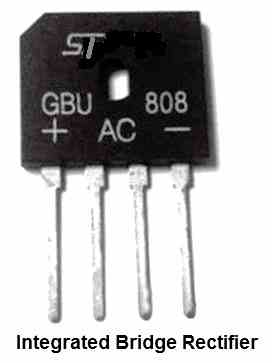
These integrated bridge rectifier come in a variety of current ratings, extending from 1A to 60A, and can tolerate PIVs ranging from 200V to 1200V. These bridge rectifiers have holea at the center to allow them to be mounted on heat sinks.
Leave a Reply